RepoGraph: Enhancing AI Software Engineering with Repository-level Code Graph
预备知识
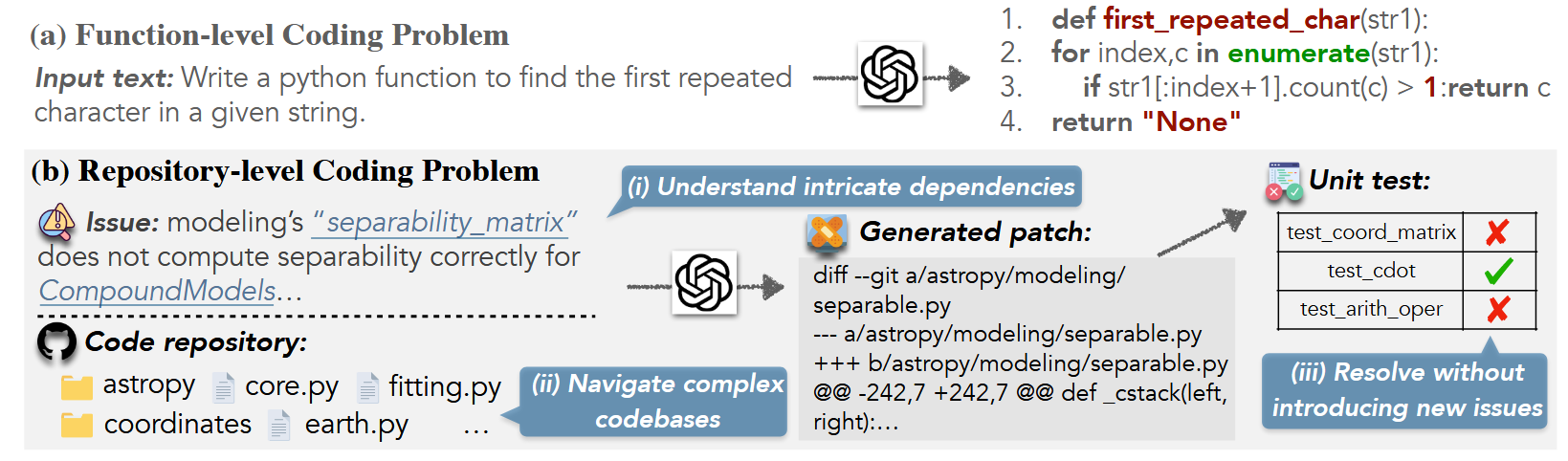
- (AI Software Engineering) 随着大模型 (LLM) 的日益发展进步, 一般的 Function-level Coding Problem (e.g., “Write a python function to find the first repeated character in a given string”) 已经完全可以交由 LLM 完成. 然而, 工业生产中的问题要复杂的多, 至少是 Repository-level Coding Problem: 由多个文件构成. 遇到的实际问题往往是需要添加某一个功能, 或者修改某一个 Bug. 这要求 LLM 1) 定位出所需要修改的位置 (File & Lines); 2) 根据整个 Repository (相当长的 Context) 来生成合适的代码.
核心思想
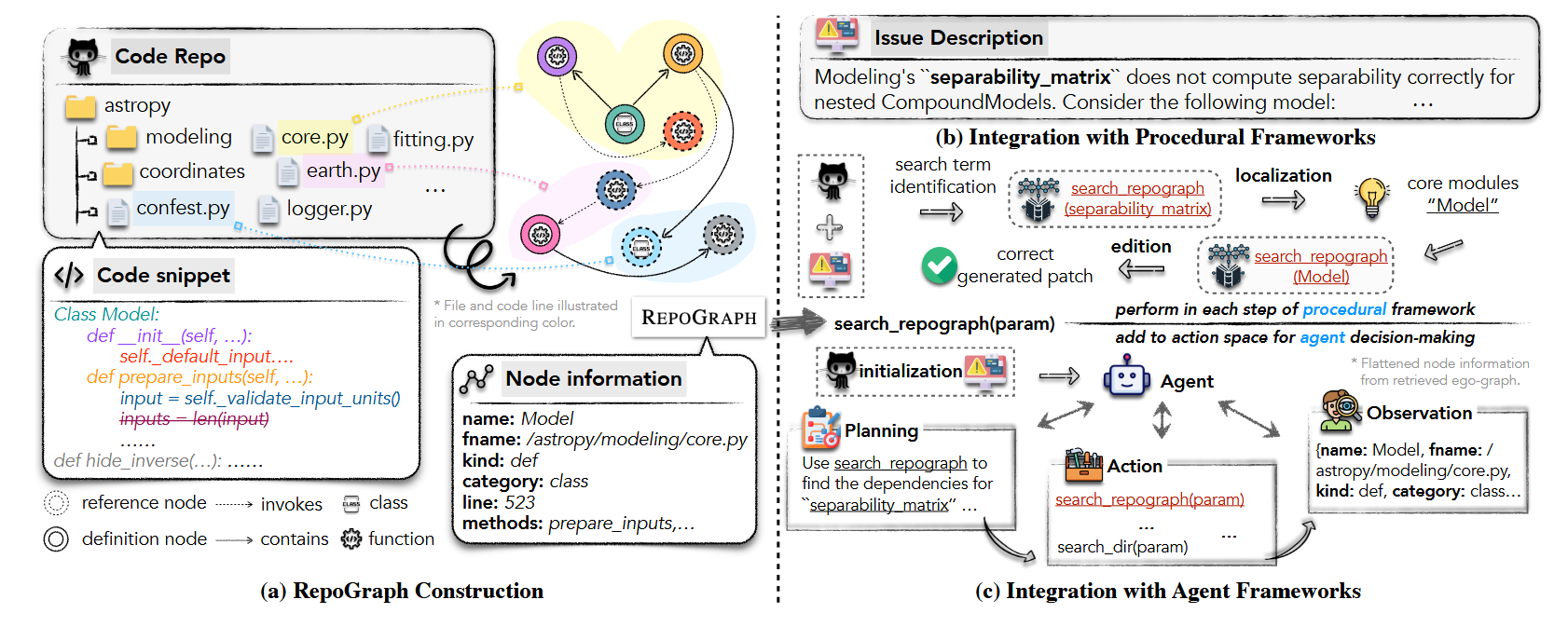
- (Code Graph) RepoGraph 按照如下的方式将一个 Repository 转成一个知识图谱, 然后借助知识图谱实现更为精准的代码生成.
- Code line parsing: RepoGraph 的每一个节点是一行代码, 通过
tree-sitter这个包来为主要的.py文件生成 Abstract Syntax Tree (AST), 基于 AST 我们可以方便地确定元素的功能: functions, classes, variables, types … - Project-dependent relation filtering: 很多元素其实和 Bug 往往没有联系, 需要移除以降低 Graph 的大小: 1) global relation: e.g., Python 的标准和内置函数; 2) local relation: 第三方库.
- Graph organization: 由此, 我们可以构建图 $\mathcal{G} = \{\mathcal{V}, \mathcal{E}\}$, 其中 $\mathcal{V}$ 表示节点 (每一个节点表示一行代码), $\mathcal{E}$ 则是节点和节点之间的关系. 节点主要包括两种类型: 1)
def(definition): 即这行代码定义了一个 function 或 class (e.g.,class Model); 2)ref(reference): 指得是这行代码是引用的其他地方已经定义好的实体. 边的类型也主要有两种: 1)contain: ($\mathcal{V}_1, \mathcal{E}_{contain}, \mathcal{V}_2$) 表示 $\mathcal{V}_1$ 包含另一个节点 $\mathcal{V}_2$ (比如, $\mathcal{V}_2$ 是 $\mathcal{V}_1$ 的一个内置方法); 2)invoke: $\mathcal{E}_{invoke}$ 通常连接def和ref, 即 reference node 依赖/引用了 definition node.
- Code line parsing: RepoGraph 的每一个节点是一行代码, 通过
注: 每个节点上附带 meta-information: line_number, file_name, directory …
- 在实际操作中, RepoGraph 提供了 search_repograph(), 给定一个 search term (往往是跟 bug 直接联系的元素), 会返回一个以 search term 为中心展开的 k-hop ego-graph, 基于这个 graph, 可以直接用 LLM, 或者 Agent 来实现更为精准的代码生成.